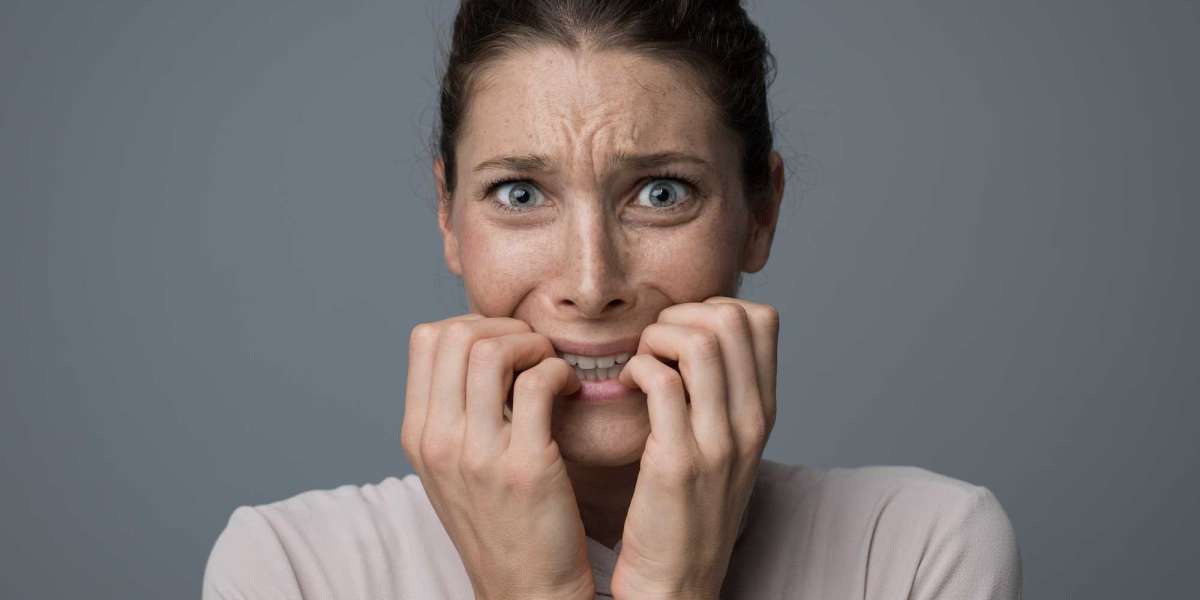
Given everything going on in today's busy world, it's common to feel overwhelmed by the never-ending list of commitments, responsibilities, and leisure activities. For those who are nervous or stressed, this mental chaos can be particularly debilitating, making it difficult to focus, stay focused, and remain productive. In order to help you regain focus and control, this post will address the challenges associated with trying to concentrate while mental turmoil is present, examine the underlying causes, and provide practical strategies for managing these symptoms.
The Impact of Stress and Anxiety on Concentration
It's common knowledge that stress and anxiety can make it difficult to concentrate, pay attention, and retain information. When the brain is subjected to excessive thoughts, concerns, and external stressors, it loses its ability to filter information and focus:
Bias in Attention:
An attentional bias caused by stress and worry might cause people to focus too much on items they perceive to be frightening or hazardous. It may be difficult to focus attention on other responsibilities or tasks as a result of this attentional constriction, which might hinder concentration.
Thinking back:
Rumination, which is characterized as persistent and uncomfortable thoughts about the past or the uncertain future, is a common indicator of worry and stress. These recurrent thoughts have the capacity to take over brain function, making it challenging to concentrate on other things or the present moment.
Excessive:
Feeling inundated with responsibilities, chores, or external stimuli can cause the brain's cognitive capacity to become overwhelmed. Focus issues and cognitive overload may arise from this. Setting priorities for your work and maintaining productivity may be challenging while you're dealing with this severe mental instability.
Physiological arousal, marked by an accelerated heart rate, shallow breathing, and stiff muscles, can be brought on by stress and anxiety. This hypervigilant state might interfere with cognitive functions, making it more difficult to concentrate, pay attention, and understand information.
The Symptoms of Cognitive Dysfunction and Lack of Concentration
Focus issues often perpetuate a vicious cycle that is made worse by mental confusion and results in emotions of annoyance, tiredness, and inadequacy:
Mental Disarray:
Distractions, internal worries, and external pressures undermine the brain's capacity to process information and maintain attention.
Having trouble concentrating:
An inability to focus exacerbates feelings of mental disorder when activities and duties pile up and productivity drops.
Increased Stress and Anxiety:
Frustration and overwhelm brought on by difficulty focusing aggravate anxiety and stress, further impairing cognitive function and escalating the vicious cycle of mental upheaval.
Reduced Efficiency:
Poor performance at work, in the school, or in daily tasks is the outcome of inability to focus. This perpetuates the stress and anxiety cycle and heightens feelings of inadequacy.
Methods for Increasing Focus and Calming Mental Chaos
While managing mental disarray and difficulties concentrating may be challenging, individuals can utilize the subsequent methods to regain clarity and focus:
To help you stay anchored in the present moment and reduce the influence of distracted thoughts and ideas that niggle at you, engage in mindfulness and grounding activities. Progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and sensory grounding exercises are some techniques to help calm and focus the mind.
Organizing tasks:
Break up responsibilities and activities into smaller, more doable portions to avoid feeling overwhelmed. Assign your projects a priority based on their importance and urgency. Make use of productivity applications, to-do lists, and calendars to manage your workload.
Effective time management:
Using time-management techniques like time-blocking or the Pomodoro Technique, plan your day and set out specific times for focused work interspersed with short breaks. By establishing realistic deadlines and goals, one can stay motivated and prevent procrastination.
Cut Down on Distractions:
To lessen distractions from your environment, set up a dedicated workstation away from noise, clutter, and interruptions. Use tools like productivity apps or website blockers to limit access to distracting websites and apps, and turn off your device's notifications.
Self-Helding:
Schedule time for self-care pursuits that promote relaxation, stress reduction, and mental wellness. Maintain a healthy diet, exercise frequently, get adequate sleep, and engage in relaxing activities like yoga or meditation to support resilience and general mental health.
Seek Assistance:
Ask friends, family, or mental health professionals for help if you're struggling to manage your stress, anxiety, or difficulty focusing. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based therapies are two types of therapy that can provide supportive and useful coping strategies for handling mental instability and improving concentration.
To sum up
Anxiety and stress-related disorders may cause trouble focusing when mental disarray occurs. By understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the cycle of mental turbulence and concentration difficulties, and putting these symptoms into practice by putting practical techniques for controlling them into practice, people can regain clarity and control over their thoughts and behaviors. Remember that you are not alone and that help is available. Never be embarrassed to seek assistance if you're struggling to manage your stress, anxiety, or lack of concentration. With perseverance, patience, and proactive self-care, mental chaos may be managed and attention can be improved to lead a more balanced and satisfying life.