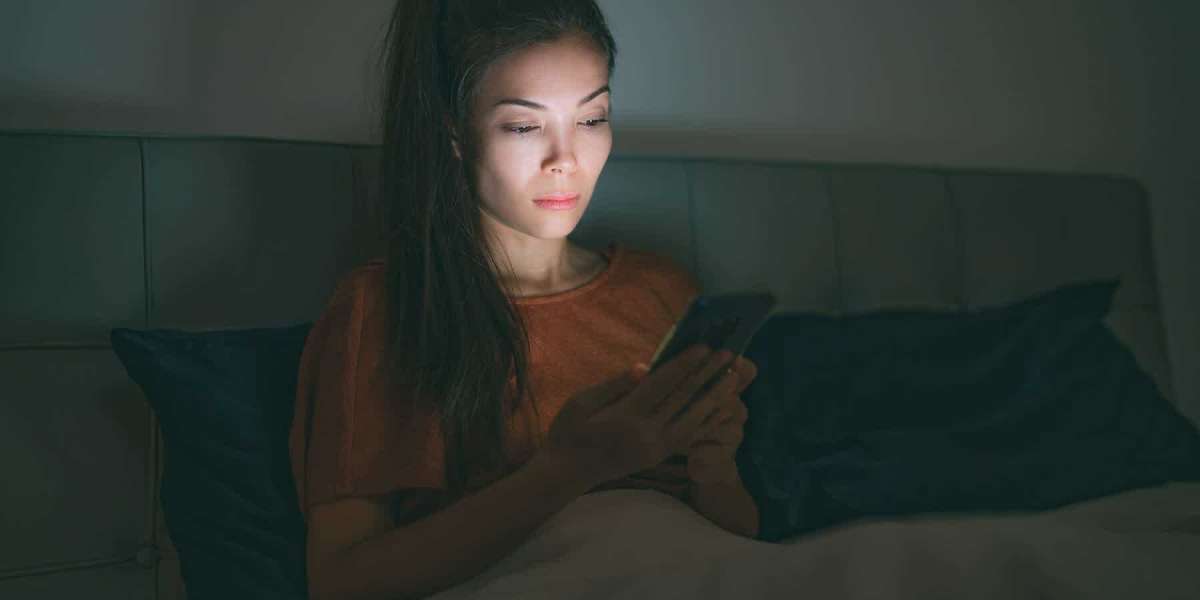
Psychophysiological insomnia is a type of sleep disorder characterized by persistent difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, often accompanied by excessive worrying about sleep. It can significantly impact one's quality of life, leading to daytime fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for psychophysiological insomnia is crucial for improving sleep health and overall well-being.
Causes of Psychophysiological Insomnia
Psychophysiological insomnia typically develops as a result of a combination of psychological, behavioral, and physiological factors. Common causes include:
Stress and Anxiety
High levels of stress or anxiety can activate the body's "fight or flight" response, making it difficult to relax and fall asleep.
Negative Sleep Associations
Negative associations with sleep or the sleep environment, such as worrying about not being able to sleep, can perpetuate insomnia.
Poor Sleep Habits
Irregular sleep schedules, excessive napping, and inconsistent bedtime routines can disrupt the body's natural sleep-wake cycle.
Hyperarousal
Individuals with psychophysiological insomnia often experience heightened arousal, both mentally and physiologically, making it challenging to initiate or maintain sleep.
Cognitive Factors
Persistent worrying or intrusive thoughts about sleep can exacerbate insomnia symptoms, creating a cycle of sleeplessness.
Symptoms of Psychophysiological Insomnia
The symptoms of psychophysiological insomnia can vary in severity and may include:
Difficulty Falling Asleep
Individuals may struggle to fall asleep within a reasonable amount of time after getting into bed.
Frequent Nighttime Awakenings
Waking up multiple times throughout the night and having difficulty returning to sleep.
Early Morning Awakening
Waking up earlier than desired and being unable to resume sleep.
Daytime Fatigue
Feeling tired and unrefreshed upon waking, leading to daytime drowsiness and reduced alertness.
Mood Disturbances
Irritability, mood swings, and heightened emotional reactivity due to poor sleep quality.
Impaired Concentration and Memory
Difficulty focusing, remembering, and performing cognitive tasks effectively during the day.
Management Strategies for Psychophysiological Insomnia
Managing psychophysiological insomnia often involves a combination of behavioral, cognitive, and lifestyle interventions. Here are some strategies that may help:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia
CBT-I is a highly effective treatment approach that addresses negative thought patterns and maladaptive behaviors associated with insomnia.
Sleep Hygiene Practices
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing the sleep environment can promote better sleep quality.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help alleviate stress and promote relaxation before bedtime.
Stimulus Control
Limiting stimulating activities in the bedroom and associating the bedroom primarily with sleep can help strengthen the association between bed and sleep.
Sleep Restriction Therapy
Gradually restricting time spent in bed to match actual sleep duration can help improve sleep efficiency and consolidate sleep.
Addressing Underlying Psychological Factors
Seeking support from a therapist or counselor to address underlying stress, anxiety, or mood disorders contributing to insomnia.
Medication Management
In some cases, short-term use of sleep medications may be prescribed to help manage insomnia symptoms, but these should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Psychophysiological insomnia can significantly impair one's ability to function during the day and negatively impact overall quality of life. By understanding the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms, and implementing effective management strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards improving sleep health and well-being. Consulting with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist can provide personalized guidance and support in managing psychophysiological insomnia effectively.